Notion에서 작성 된 글입니다. 템플릿이 깨진다면 Notion을 확인해주세요.
Redis의 분산 락을 적용하고 Pub/Sub로 동시성 문제를 해결하자. | Notion
들어가기앞서…
hail-buttercup-c86.notion.site
들어가기 앞서 . . .
프로젝트에서 동시성 문제를 해결하기 위해 락에 대해서 공부하고, 또 성능 개선을 위해 고민까지 해보았다.
하지만 결국 락을 걸고 동시성을 해결한다는 것은, 하나의 요청을 처리하는 동안 모든 요청이 대기를 하기때문에 성능이 눈에띄게 좋아지는 것은 힘들 것 같다는 생각이 들었다.
성능을 개선하기위해 구글링을 하니 ‘분산 락’이라는 것에 대한 언급이 많았다. 분산 락은 무엇일까? 한 번 알아보자.
분산 락
분산락은 분산 시스템에서 여러 노드나 프로세스가 동시에 공유 자원에 접근할 때 발생하는 충돌을 방지하고, 자원의 일관성을 유지하기 위해 사용되는 기술이다.
분산 락의 종류
분산 락을 구현할 수 있는 방식은 여러가지가 존재한다.
분산 락 구현에는 Redis, MySQL의 네임드 락, 그리고 ZooKeeper 등의 기술이 사용되며, Redis는 주로 SETNX 명령어와 Redlock 알고리즘을 통해, MySQL은 자체적으로 제공하는 네임드 락을 활용해 동시성 문제를 해결한다.
분산 락 적용 이유
하지만 필자가 진행중인 프로젝트는 단일 서버인데도 Redis 분산 락을 적용하기로했다.
1. 커넥션 풀 / 자원 고갈 방지
현재 select … for update문으로 요청이 몰릴 시, 모든 요청이 DB 커넥션을 붙잡고 대기하게 된다. 때문에 커넥션 풀 고갈이 일어나 timeout 시간이 지나면 예외가 발생하게 된다.
Redis는 DB랑 별도로 ‘락’만 관리하기때문에, Redis 연결은 메인 DB의 커넥션과 별도로 관리된다. 락을 흭득 가능할 경우에만 DB 커넥션을 사용해 작업을 처리하고, 흭득하지 못한 경우에는 DB 커넥션을 사용하지 않고 대기해 DB 커넥션 풀에 영향을 주지 않는다.
2. 후의 인스턴스 확장 대비
Redis 분산 락을 구현할 시, 모든 애플리케이션 인스턴스가 동일한 Redis 서버를 바라보므로 일관된 락 상태를 유지하여 확장성에 영향을 받지 않는다.
현재는 단일 서버지만, 다중 서버로 늘릴 가능성이 존재해 분산 락을 구현하기로 결정하였다.
Redis 설정하기
의존성 추가
Redisson을 사용하기 위해 의존성을 추가해주자. 아래의 공식문서를 통해서 최신 redisson dependency를 확인할 수 있다.
// Gradle
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-data-redis:3.5.5'
implementation group: 'org.redisson', name: 'redisson-spring-boot-starter', version: '3.51.0'
//Maven
<dependency>
<groupId>org.redisson</groupId>
<artifactId>redisson</artifactId>
<version>3.51.0</version>
</dependency>
Getting Started - Redisson Reference Guide
Getting Started - Redisson Reference Guide
Getting Started Add dependency Redisson PRO Maven pro.redisson redisson 3.52.0 Gradle compile 'pro.redisson:redisson:3.52.0' Community Edition Maven org.redisson redisson 3.52.0 Gradle compile 'org.redisson:redisson:3.52.0' Redisson PRO vs. Community Editi
redisson.pro
application.yml
host와 port모두 기본적인 Redis 값을 넣어주었기때문에, 따로 포트를 변경했다면 변경한 포트번호를 넣어주면 된다.
spring:
redis:
host: localhost
port: 6379
Redis를 사용하기 위해 간단한 코드 및 설정파일을 구현하였다.
RedisConfig
@Configuration
public class RedisConfig {
@Value("${spring.redis.host}")
private String host;
@Value("${spring.redis.port}")
private int port;
private static final String REDISSON_HOST_PREFIX = "redis://";
@Bean
public RedissonClient redissonClient() {
Config config = new Config();
config.useSingleServer().setAddress(REDISSON_HOST_PREFIX + host + ":" + port);
return Redisson.create(config);
}
@Bean
public RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory() {
return new LettuceConnectionFactory(host, port);
}
/**
* Redis 데이터 처리를 위한 템플릿을 구성합니다.
* 해당 구성된 RedisTemplate을 통해서 데이터 통신으로 처리되는 대한 직렬화를 수행합니다.
*
* @return RedisTemplate<String, Object>
*/
@Bean
public RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate() {
RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate = new RedisTemplate<>();
// Redis를 연결합니다.
redisTemplate.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory());
// Key-Value 형태로 직렬화를 수행합니다.
redisTemplate.setKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
redisTemplate.setValueSerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
// Hash Key-Value 형태로 직렬화를 수행합니다.
redisTemplate.setHashKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
redisTemplate.setHashValueSerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
// 기본적으로 직렬화를 수행합니다.
redisTemplate.setDefaultSerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
return redisTemplate;
}
/**
* 리스트에 접근하여 다양한 연산을 수행합니다.
*
* @return ListOperations<String, Object>
*/
public ListOperations<String, Object> getListOperations() {
return this.redisTemplate().opsForList();
}
/**
* 단일 데이터에 접근하여 다양한 연산을 수행합니다.
*
* @return ValueOperations<String, Object>
*/
public ValueOperations<String, Object> getValueOperations() {
return this.redisTemplate().opsForValue();
}
/**
* Redis 작업중 등록, 수정, 삭제에 대해서 처리 및 예외처리를 수행합니다.
*
* @param operation
* @return
*/
public int executeOperation(Runnable operation) {
try {
operation.run();
return 1;
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Redis 작업 오류 발생 :: " + e.getMessage());
return 0;
}
}
@Bean
public RTopic ticketTopic(RedissonClient redissonClient) {
return redissonClient.getTopic("ticketEvent", new JsonJacksonCodec());
}
}
RedisSingleDataController
/**
* Redis 단일 데이터를 조회, 등록, 삭제하는 로직입니다.
*
* @author : jonghoon
* @fileName : RedisSingleDataController
* @since : 11/5/24
*/
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/v1/redis/singleData")
public class RedisSingleDataController {
private final RedisSingleDataService redisSingleDataService;
public RedisSingleDataController(RedisSingleDataService redisSingleDataService) {
this.redisSingleDataService = redisSingleDataService;
}
/**
* Redis 키를 기반으로 단일 데이터의 값을 조회합니다.
*
* @param redisDto
* @return
*/
@PostMapping("/getValue")
public ResponseEntity<Object> getValue(@RequestBody RedisDto redisDto) {
String result = redisSingleDataService.getSingleData(redisDto.key());
return new ResponseEntity<>(result, HttpStatus.OK);
}
/**
* Redis 단일 데이터 값을 등록/수정합니다.(duration 값이 존재하면 메모리 상 유효시간을 지정합니다.)
*
* @param redisDto
* @return
*/
@PostMapping("/setValue")
public ResponseEntity<Object> setValue(@RequestBody RedisDto redisDto) {
int result = 0;
if (redisDto.duration() == null) {
result = redisSingleDataService.setSingleData(redisDto.key(), redisDto.value());
} else {
result = redisSingleDataService.setSingleData(redisDto.key(), redisDto.value(), redisDto.duration());
}
return new ResponseEntity<>(result, HttpStatus.OK);
}
/**
* Redis 키를 기반으로 단일 데이터의 값을 삭제합니다.
*
* @param redisDto
* @return
*/
@DeleteMapping("/delete")
public ResponseEntity<Object> deleteRow(@RequestBody RedisDto redisDto) {
int result = redisSingleDataService.deleteSingleData(redisDto.key());
return new ResponseEntity<>(result, HttpStatus.OK);
}
}
RedisHandler
@Component
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class RedisHandler {
private final RedisConfig redisConfig;
/**
* 리스트에 접근하여 다양한 연산을 수행합니다.
*
* @return ListOperations<String, Object>
*/
public ListOperations<String, Object> getListOperations() {
return redisConfig.redisTemplate().opsForList();
}
/**
* 단일 데이터에 접근하여 다양한 연산을 수행합니다.
*
* @return ValueOperations<String, Object>
*/
public ValueOperations<String, Object> getValueOperations() {
return redisConfig.redisTemplate().opsForValue();
}
/**
* Redis 작업중 등록, 수정, 삭제에 대해서 처리 및 예외처리를 수행합니다.
*
* @param operation
* @return
*/
public int executeOperation(Runnable operation) {
try {
operation.run();
return 1;
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Redis 작업 오류 발생 :: " + e.getMessage());
return 0;
}
}
}
RedisSingleDataServiceImpl
@Service
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class RedisSingleDataServiceImpl implements RedisSingleDataService {
private final RedisHandler redisHandler;
private final RedisConfig redisConfig;
/**
* Redis 단일 데이터 값을 등록/수정합니다.
*
* @param key : redis key
* @param value : redis value
* @return {int} 성공(1), 실패(0)
*/
@Override
public int setSingleData(String key, Object value) {
return redisHandler.executeOperation(() -> redisHandler.getValueOperations().set(key, value));
}
/**
* Redis 단일 데이터 값을 등록/수정합니다.(duration 값이 존재하면 메모리 상 유효시간을 지정합니다.)
*
* @param key : redis key
* @param value: : redis value
* @param duration : redis 값 메모리 상의 유효시간.
* @return {int} 성공(1), 실패(0)
*/
@Override
public int setSingleData(String key, Object value, Duration duration) {
return redisHandler.executeOperation(() -> redisHandler.getValueOperations().set(key, value, duration));
}
/**
* Redis 키를 기반으로 단일 데이터의 값을 조회합니다.
*
* @param key : redis key
* @return {String} redis value 값 반환 or 미 존재시 null 반환
*/
@Override
public String getSingleData(String key) {
if (redisHandler.getValueOperations().get(key) == null) return "";
return String.valueOf(redisHandler.getValueOperations().get(key));
}
/**
* Redis 키를 기반으로 단일 데이터의 값을 삭제합니다.
*
* @param key : redis key
* @return {int} 성공(1), 실패(0)
*/
@Override
public int deleteSingleData(String key) {
return redisHandler.executeOperation(() -> redisConfig.redisTemplate().delete(key));
}
}
RedisDto
public record RedisDto (
String key,
String value,
Duration duration
){}
Pub/Sub로 동시성을 해결해보자.
필자의 이벤트 응모 로직을 보면 아래와 같다.
꽝 로직
이벤트 참여 → 포인트 차감 → 이벤트 누적 금액 증가 → 포인트 결제 내역 발급 → 우승자 여부 판단 → 응답
당첨 로직
이벤트 참여 → 포인트 차감 → 이벤트 누적 금액 증가 → 포인트 결제 내역 발급 → 우승자 여부 판단 → 이벤트 마감 → 예매권 발급 → 멤버에게 지급
TicketLockMessage
이벤트에 응모하고, 포인트 차감 및 누적을 하기 위해서는 누가 어떤 이벤트에 참여했는 지 알아야한다.
Publisher → Subscriber 간에 주고받는 메시지 DTO이다.
@Getter
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
@JsonTypeInfo(
use = JsonTypeInfo.Id.CLASS,
include = JsonTypeInfo.As.PROPERTY,
property = "@class"
)
public class TicketLockMessage{
Long eventId;
Long memberId;
}
EventServiceImpl
applyTicketEvent 메서드가 호출되면 SecurityUtil.getSignInMemberId() 메서드를 통해 현재 로그인한 사용자의 id를 가져와, 이벤트 id와 사용자 id를 담아 메세지 객체를 생성한다.
즉, 어떤 이벤트에 어떤 사용자가 응모하는지 담는 객체이다.
이후에 EventPublisher를 통해 Redis Pub/Sub topic으로 메시지를 발행한다.
eventPublisher 내부에서는 RTopic.publishAsync(msg)를 호출해서 Redis에 메시지를 브로드캐스트한다.
@Service
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class EventServiceImpl implements EventService {
private final EventPublisher eventPublisher;
...
@Override
public void applyTicketEvent(Long eventId) {
Long memberId = SecurityUtil.getSignInMemberId();
TicketLockMessage msg = new TicketLockMessage(
eventId,
memberId
);
eventPublisher.publish(msg);
}
}
EventPublisher
이벤트를 발행해서 여러 구독자에게 비동기적으로 알리는 코드이다.
Redis의 ticket-event-topic 토픽을 얻어, TicketLockMessage를 비동기(async)로 발한다.
@Slf4j
@Service
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class EventPublisher {
private final RedissonClient redissonClient;
private static final String TOPIC_NAME = "ticket-event-topic";
public void publish(TicketLockMessage msg) {
RTopic topic = redissonClient.getTopic(TOPIC_NAME, new JsonJacksonCodec());
topic.publishAsync(msg)
.thenAccept(r -> log.info("Published ticket event: {}", msg));
}
}
RTopic topic = redissonClient.getTopic(TOPIC_NAME, new JsonJacksonCodec());
topic.publishAsync(msg)
.thenAccept(r -> log.info("Published ticket event: {}", msg));
EventSubscriber
publisher로부터 알림을 받으면 실행된다. 이벤트 응모 요청을 보냈을 때, Redis Pub/Sub + 분산 락으로 순차 처리하도록 만든 구독자 서비스이다.
@Slf4j
@Service
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class EventSubscriber {
private final RedissonClient redissonClient;
private final EventCoreLockService coreLockService;
private final PostActionsService postActionsService;
private static final String TOPIC_NAME = "ticket-event-topic";
@PostConstruct
public void subscribe() {
RTopic topic = redissonClient.getTopic(TOPIC_NAME, new JsonJacksonCodec());
topic.addListener(TicketLockMessage.class, (channel, msg) -> {
log.info("Received ticket event message: {}", msg);
String lockName = "ticket-lock:" + msg.getEventId();
RLock lock = redissonClient.getLock(lockName);
// 최대 5초 대기, 자동 해제 10초
lock.lockAsync(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS).thenRunAsync(() -> {
try {
// 이벤트 응모
EventDecision decision = coreLockService.applyCore(msg.getEventId(), msg.getMemberId());
// 후속 처리(포인트 결제내역 및 우승 여부)
postActionsService.recordPointHistory(msg.getMemberId(), decision.perPrice(), PointTarget.EVENT);
if (decision.winner()) {
postActionsService.reserveSeatAndCreateReservation(
decision.seatId(), msg.getMemberId(), decision.perPrice());
}
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("Error processing ticket event: {}", e.getMessage(), e);
} finally {
lock.unlockAsync();
}
});
});
}
}
핵심 코드는 아래와 같다.
topic.addListener(TicketLockMessage.class, (channel, msg) -> {
log.info("Received ticket event message: {}", msg);
TicketLockMessage 타입의 메시지가 도착하면 실행한다.
분산 락 흭득
String lockName = "ticket-lock:" + msg.getEventId();
RLock lock = redissonClient.getLock(lockName);
// 최대 5초 대기, 자동 해제 10초
lock.lockAsync(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS).thenRunAsync(() -> {
eventId별로 고유한 락을 생성한다. (ticket-lock:1, ticket-lock:2 같은 형태)
lock.lockAsync(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS) → 락을 잡고 10초 후 자동 해제(lease time)하여, 다른 서버/스레드가 동시에 같은 이벤트에 접근 못하도록 보장한다.
thenRunAsync: 락을 잡은 뒤, 비동기로 로직을 실행한다.
try {
EventDecision decision = coreLockService.applyCore(msg.getEventId(), msg.getMemberId());
postActionsService.recordPointHistory(msg.getMemberId(), decision.perPrice(), PointTarget.EVENT);
if (decision.winner()) {
postActionsService.reserveSeatAndCreateReservation(
decision.seatId(), msg.getMemberId(), decision.perPrice());
}
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("Error processing ticket event: {}", e.getMessage(), e);
} finally {
lock.unlockAsync();
}
- coreLockService.applyCore(...) → 이벤트 참여 처리한다. (포인트 차감, 이벤트 금액 누적, 당첨자 결정).
- recordPointHistory(...) → 포인트 차감 내역을 기록한다.
- 당첨자라면 reserveSeatAndCreateReservation(...) → 좌석 상태를 예약으로 바꾸고 예약(예매권) 엔티티 생성 및 발급한다.
finally에서 무조건 lock이 해제되게하였다.
EventCoreLockService
우리 서비스 이벤트 응모의 비즈니스 로직이다. 각자 서비스의 핵심 로직을 넣어주면 된다.
Redis pub/sub와 관련된 부분은 없으므로 간단하게 설명하자면 회원이 이벤트 티켓 응모를 했을 때 → 포인트 차감 → 이벤트 금액 누적 → 당첨 여부 판정을 한다.
@Service
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class EventCoreLockService {
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW)
public EventDecision applyCore(Long eventId, Long memberId) {
...
}
}
PostActionsService
우리 서비스 이벤트 응모 처리 이후에 해야 할 후속 작업을 모아둔 Service이다.
Redis pub/sub와 관련된 부분은 없으므로 간단하게 설명하자면 핵심 비즈니스 로직(EventCoreLockService)이 끝난 뒤, 그 결과에 따라 포인트 내역 저장과 좌석 예약 처리를 담당한다.
@Slf4j
@Service
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class PostActionsService {
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW)
public void recordPointHistory(Long memberId, int amount, PointTarget target) {
...
}
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW)
public void reserveSeatAndCreateReservation(Long seatId, Long memberId, int accrued) {
...
}
}
결과
Redis 분산 락(pub/sub) 적용 전과 후를 비교해보았다.
기존의 Redis를 적용하지 않고 비관적 락을 통해서 10초동안 1초에 1000명 요청을 보내도록 하였을 때의 모니터링 결과이다.
DB Connection을 24로 고정하고, connection timeout을 3초로 뒀었다.

뿐만 아니라, 10초동안 1초에 100명의 요청을 보낼 때도, 10% 이내의 오류가 검출되었었다. (timeout 오류였다.)
커넥션 타임 아웃을 길게 설정하니 작은 요청에는 응답이 잘 돌아오나, 요청수를 높였더니 특정 구간에서 작업이 멈춘 것 처럼 보이는 현상이 있어, timeout을 다시 짧게 두고 분산 락을 적용하게 되었다.
Redis 분산락 pub/sub 적용 이후
1000명은 가볍게 성공한다.

표본수 1000일 때, 1초당 101개를 처리한다.(tps: 101)

요청 수를 늘려 10000개의 요청을 보내보자.

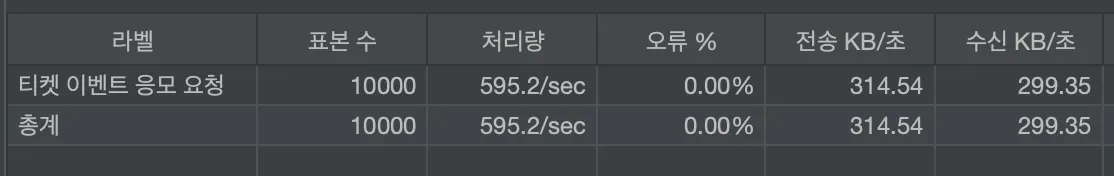
표본수 1000일 때, 1초당 595개를 처리한다.(tps: 595)
마무리하며...
이번 과정을 통해 단순히 락을 걸면 동시성이 해결된다는 생각이 얼마나 위험할 수 있는지 깨달았다.
DB 비관적 락만으로는 커넥션 풀 고갈과 같은 자원 문제를 피할 수 없었고, 실제로 대규모 요청이 몰릴 경우 예외가 발생하며 서비스 안정성이 무너졌다.
Redis 분산 락과 Pub/Sub을 적용하면서 핵심 로직은 직렬화하여 정합성을 보장하고, 후속 처리(내역 기록·좌석 예약)는 비동기로 분리하는 구조를 만들 수 있었다.
이를 통해 커넥션 풀 고갈 문제를 방지하고, 동시에 성능(TPS)도 크게 개선할 수 있었다.
하지만 Pub/Sub에 대해 추가적으로 공부하면서, 우리 서비스에는 맞지 않다는 점도 알게 되었다.
현재 프로젝트는 선착순 응모라는 특성상 순차성이 보장되어야 하는데, Pub/Sub은 메시지 순서를 보장하지 않는다. 또한 메시지가 유실되면 “응모는 성공했지만 포인트가 차감되지 않거나, 포인트는 차감되었지만 누적이 반영되지 않는” 치명적인 오류가 발생할 수 있다.
결국 Pub/Sub은 데이터 유실이 되어도 큰 피해가 없는 알림·로그성 이벤트에는 적합하지만, 티켓 서비스와 같은 정합성이 중요한 비즈니스 로직에는 부적합하다는 결론을 내렸다.
이번 경험에서 얻은 가장 큰 교훈은 “성능 개선은 단순히 락을 도입하는 것이 아니라, 어떤 자원에 락을 걸고 어떻게 병렬화를 유지할지 설계하는 과정”이라는 점이다.
Redis Stream, Kafka와 같은 순차성과 내구성을 보장할 수 있는 메시지 큐를 검토하며, 정합성과 성능 사이의 균형을 고민해야겠다는 생각을 하게 되었다.
'Spring' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [ Spring ] 비관적 락 성능 개선을 해보자 (0) | 2025.09.30 |
|---|---|
| [ Spring ] 동시성을 잠금으로 안전하게 처리해보자 (0) | 2025.09.19 |
| [SQL]Error: 1406-22001: Data too long for column '?' at row 1 (0) | 2024.10.01 |
| [Spring Security] Security 기본 (0) | 2024.08.29 |
| [Spring] 컨트롤러 예외처리(Exception Handling) (0) | 2024.07.21 |
